Thermal Insulation Glass
Overview
Today's building codes, homeowners and communities are demanding more from glass. In particular, the focus on energy efficiency and tighter regulations are creating a greater need for low-emissivity (low-e) glass. Through advances in low-e glass, windows now play a big part in energy conservation and comfort, minimizing heat loss and internal condensation.
With our wide range of low-emissivity glass we can meet all your energy saving requirements.
How it works
Low-e glass reduces the heat loss of the building by:
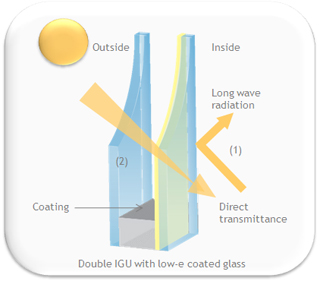
(1) Reflecting the energy emitted by room heaters and surfaces back into the room (long wave radiation).
(2) Allowing high transmission of the solar radiation (short wave radiation) through the glass to benefit from passive solar heat gain through the glass.
During the winter, low-emissivity (low-e) glass can reduce heat loss while allowing high levels of valuable free solar gain to heat buildings with no significant loss in natural light.
Low-E 4th Surface Technology
Pilkington Low-E 4th Surface Technology allows double-glazed insulated glass units to achieve better thermal performance. Applying two pyrolytic low-e lites in an insulated glass unit reduces the center-of-glass u-factor by 45%, compared to a unit with two panes of standard clear glass.
- In cold weather conditions, the pyrolytic low-e coating on the #2 surface reduces room heat from transferring across the airspace toward the outside. By adding a second low-e coating to the #4 surface the thermal insulation is improved.
- A low-e coating on the #4 surface reflects room heat, back inside in cold weather conditions. This reduces the radiant heat loss and improves the overall insulation of the unit.